Prions, Viroids and Virusoids
_
Prions
What exactly are Prions?
Prions are rogue or bad protein which have abnormal structures, the mis-folded form of the protein can alter other cellular proteins ( PrPC) to the prion form PrPSc.
This tree diagram shows the different types of prions
How do prions transform other cellular proteins?
The prions simply uses it’s abnormal structure to convert normal molecules to the abnormally structured form.Once the normal cells get infected, they don’t work properly or otherwise, don’t work at all.The infected cells are stable and accumulates until the cells die off.
Once the cells die, they releases prions into the blood stream to infect more cells. Even though these cells are protein cells, they are resistant to heat and denaturation.Their resistance makes them difficult to be removed or killed.
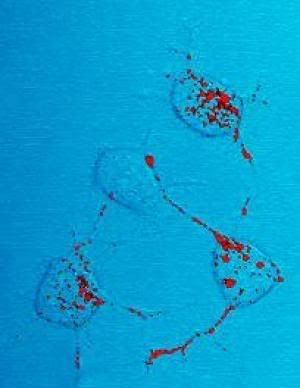
Picture showing prions infecting a cell.
Pathogenesis:
They are Spongiform encephalitis. They look like “sick” brains riddled with holes and they resemble Swiss cheese.
An experiment to test on convertion:
- Firstly, 2 mice are prepared, 1 with knockout PrPc gene, and the other with normal PrPc gene.
- The mouse with normal gene will produce PrPc protein while the other without will not.
- Next, both mice are infected with prions. The prions will infect the mouse with PrPc proteins but not the mouse without it since it has nothing to convert.
- Eventually the mouse with PrPc proteins dies.
- This is because in order for the prions to cause harm and damage to the cells.
- The prions must first convert the normal PrPc to rogue proteins.
Viroids
What are viroids?
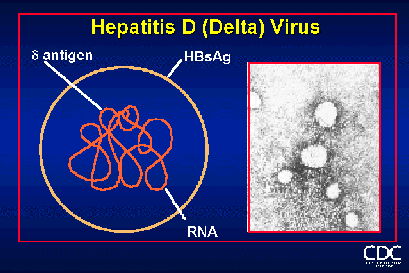
Viroids are infectious agents composed of a single stranded circular RNA which consist of some double-stranded regions.They can be considered as 1 of the smallest known virus capable of causing disease.
Viroids mostly affect plants such as fungi etc. There is only 1 human pathogen known to cause disease in human, and that is Hepatitis D.
Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D is a disease caused by small RNA viruses which is also known as delta agent virus.The hepatitis D viroid RNA affects the human liver cell 7S RNA.The virus kills the liver cell by cleaving it and altering the shape of the cell.The person infected with Hepatitis D will suffer from chronic liver infections.
Among all the hepatitis infection, hepatitis D has the highest mortality rate of all. Transmission of this virus can be done by unprotected sex, sharing of contaminated needles and close contact.
Prevention of spreading can be done by using clean and sterile needles, and having safe sex.
Virusoid
Virusoid is an infectious agent that will infect plants with another allying virus.
They are single stranded circular RNA which depends on plants for replication.
It has several hundreds of nucleotides and only encodes structural proteins.Virusoids are similar to viroids, in comparison of size, shape or replication technique.
Although virusoids are studied under virology, they are not classified as virus but as a subviral particle.
Videos:
This video explains how do prions arise and gives more information about them.
References:
HELLO
2:12 AM
2:12 AM